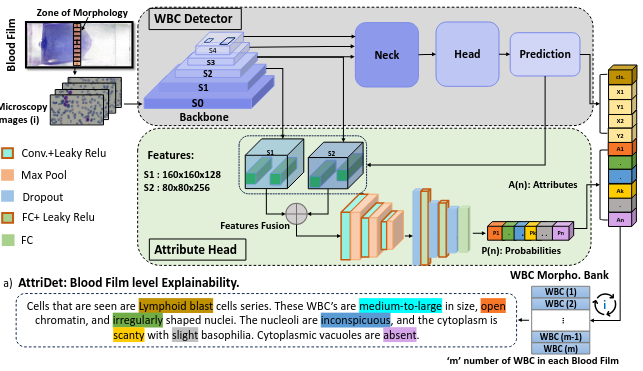
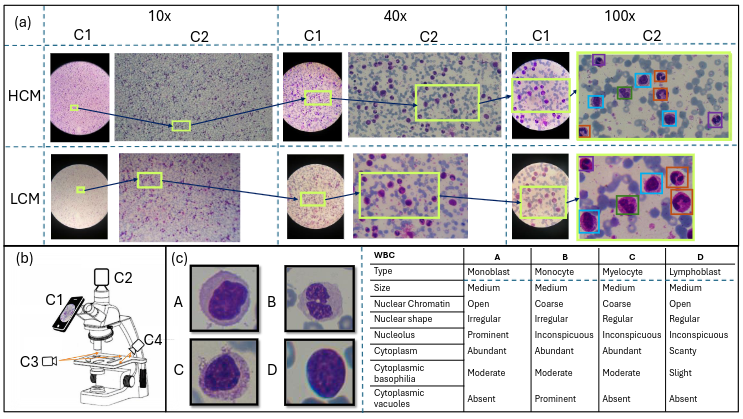
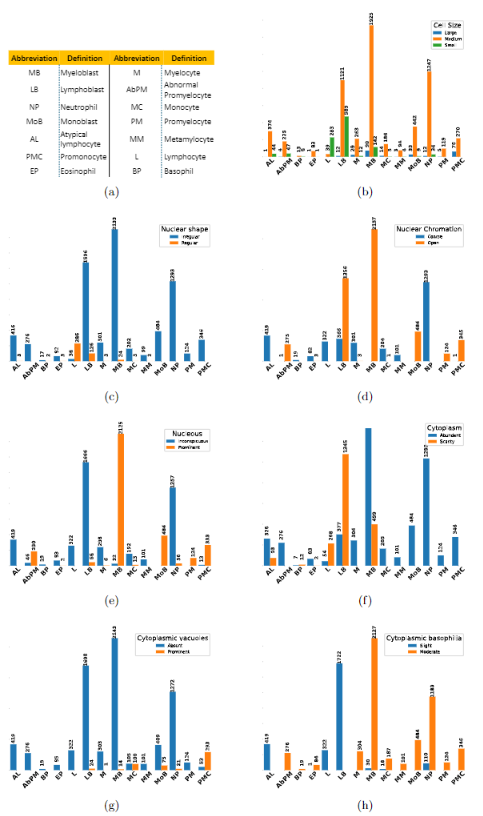
Earlier diagnosis of Leukemia can save thousands of lives annually. The prognosis of leukemia is challenging without the morphological information of White Blood Cells (WBC) and relies on the accessibility of expensive microscopes and the availability of hematologists to analyze Peripheral Blood Samples (PBS). Deep Learning based methods can be employed to assist hematologists. However, these algorithms require a large amount of labeled data, which is not readily available. To overcome this limitation, we have acquired a realistic, generalized, and large dataset. To collect this comprehensive dataset for real-world applications, two microscopes from two different cost spectrums (high-cost HCM and low-cost LCM) are used for dataset capturing at three magnifications (100x, 40x, 10x) through different sensors (high-end camera for HCM, middle-level camera for LCM and mobile-phone camera for both). The high-sensor camera is 47 times more expensive than the middle-level camera and HCM is 17 times more expensive than LCM. In this collection, using HCM at high resolution (100x), experienced hematologists annotated 10.3k WBC types (14) and artifacts, having 55k morphological labels (Cell Size, Nuclear Chromatin, Nuclear Shape, etc.) from 2.4k images of several PBS leukemia patients. Later on, these annotations are transferred to other 2 magnifications of HCM, and 3 magnifications of LCM, and on each camera captured images. Along with the LeukemiaAttri dataset, we provide baselines over multiple object detectors and Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) strategies, along with morphological information-based attribute prediction. The dataset will be publicly available after publication to facilitate the research in this direction.